Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate a computer-aided diagnostic system using texture analysis to improve radiologic accuracy for identification of thyroid nodules as malignant or benign.
Methods
The database comprised 26 benign and 34 malignant thyroid nodules. Wavelet transform was applied to extract texture feature parameters as descriptors for each selected region of interest in 3 normalization schemes (default, μ ± 3σ, and 1%–9%). Linear discriminant analysis and nonlinear discriminant analysis were used for texture analysis of the thyroid nodules. The first–nearest neighbor classifier was applied to features resulting from linear discriminant analysis. Nonlinear discriminant analysis features were classified by using an artificial neural network. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to examine the performance of the texture analysis methods.
Results
Wavelet features under default normalization schemes from nonlinear discriminant analysis indicated the best performance for classification of benign and malignant thyroid nodules and showed 100% sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy; the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 1.
Conclusions
Wavelet features have a high potential for effective differentiation of benign from malignant thyroid nodules on sonography.
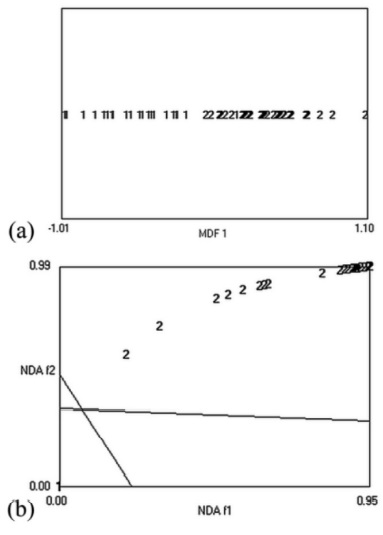
discriminant analysis (a) and nonlinear discriminant analysis (NDA; b).
Areas on the nonlinear discriminant analysis (f1 and f2) plane that form
a common part of sets belong to 2 different categories (benign and
malignant nodules). MDF indicates most discriminating features.

