Abstract
Background
ChatGPT is a large language model (LLM) artificial intelligence instrument trained on massive amounts of text data extracted from the internet and/or user input. In the present article, we aim to apply the latest version of ChatGPT to the Iranian Medical Residency Examination.
Methods
The Iranian Medical Residency Examination is composed of 200 multichoice questions covering all domains of medicine. We used ChatGPT to translate questions into English, French, and Spanish. We fed the questions as multiple-choice questions and allowed ChatGPT to provide comprehensive answers and justifications for its choices.
Results
ChatGPT was able to answer 161 (81.3% = 161/198) questions correctly when the Persian language was used. When the questions were translated into English, French, and Spanish, ChatGPT answered six, one, and five additional questions correctly, respectively. When comparing the different languages, there was no significant difference in the functioning of ChatGPT in different languages using either the McNemar test or the Binomial test.
Conclusion
ChatGPT can deliver above-average performance in the Iranian Medical Residency Examination, demonstrating its potential for using language models in medicine.
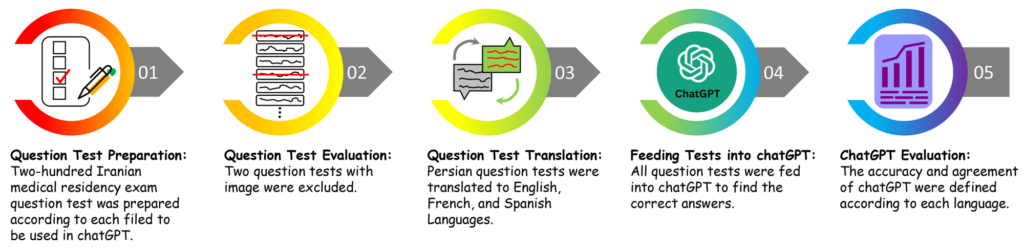
Flow chart of the study highlighting the five main phases of the methodology.

