Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate computer aided diagnosis (CAD) system with texture analysis (TA) to improve radiologists’ accuracy in identification of thyroid nodules as malignant or benign.
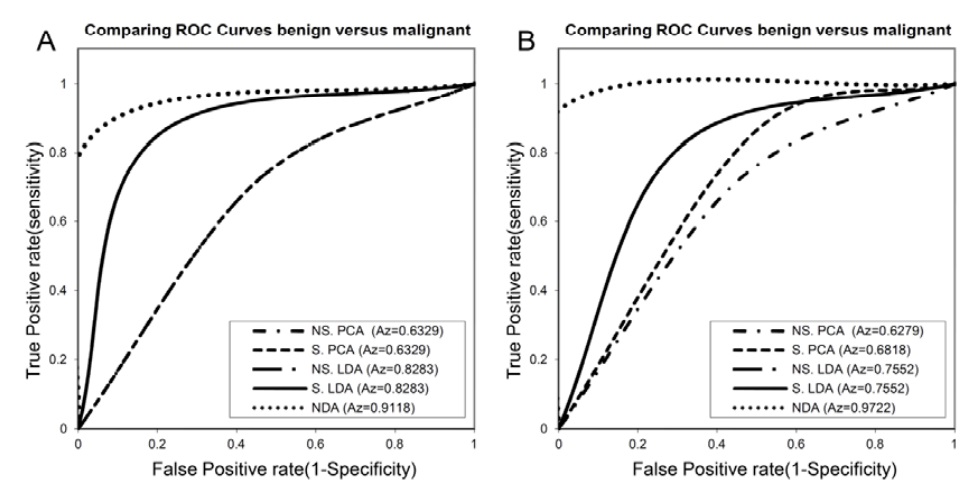
Methods: A total of 70 cases (26 benign and 44 malignant) were analyzed in this study. We extracted up to 270 statistical texture features as a descriptor for each selected region of interests (ROIs) in three normalization schemes (default, 3σ and 1%-99%). Then features by the lowest probability of classification error and average correlation coefficients (POE+ACC), and Fisher coefficient (Fisher) eliminated to 10 best and most effective features. These features were analyzed under standard and nonstandard states. For TA of the thyroid nodules, Principle Component Analysis (PCA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) and Non-Linear Discriminant Analysis (NDA) were applied. First Nearest-Neighbour (1-NN) classifier was performed for the features resulting from PCA and LDA. NDA features were classified by artificial neural network (A-NN). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used for examining the performance of TA methods.
Results: The best results were driven in 1-99% normalization with features extracted by POE+ACC algorithm and analyzed by NDA with the area under the ROC curve (Az) of 0.9722 which correspond to sensitivity of 94.45%, specificity of 100%, and accuracy of 97.14%.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that TA is a reliable method, can provide useful information help radiologist in detection and classification of benign and malignant thyroid nodules.