Abstract
The scaphoid is one of the most common carpal bone fractures diagnosed using radiographs. However, occult scaphoid fractures not visible on radiographs make early diagnosis and treatment difficult. Hence, the objective of this study was to develop a high-performing deep-learning model for the detection of apparent fracture and non-apparent occult scaphoid fractures using only plain wrist radiographs. This work used 525 x-ray images, 250 of which were normal scaphoids, 219 were fractured scaphoids, and 56 were occult fracture X-rays. These X-ray images were obtained from the Department of Orthopaedics, Kasturba Medical College’s (KMC), Manipal. A CNN-based deep learning model was developed for two classes (normal VS fracture) and three classes (normal VS fracture VS occult). For fracture localization, gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) was used. For two-class classification, the proposed CNN model achieved sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and AUC of 92%, 88%, 90% and 0.95, respectively. For three-class classification, the proposed model achieved an overall performance of 85% sensitivity, 91% specificity, 90% accuracy and 0.88 AUC. Wrist radiograph images used to train the model did not undergo a segmentation process, saving time and improving efficiency if implemented in a hospital setting.
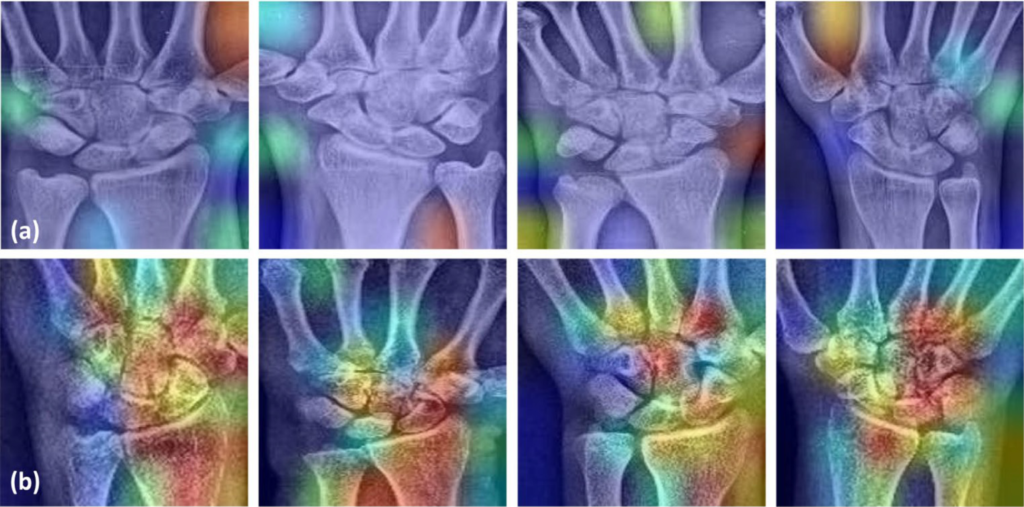
Gradient-weighted class activation map (Grad-CAM) samples for control (a) and fracture (b) cases.

