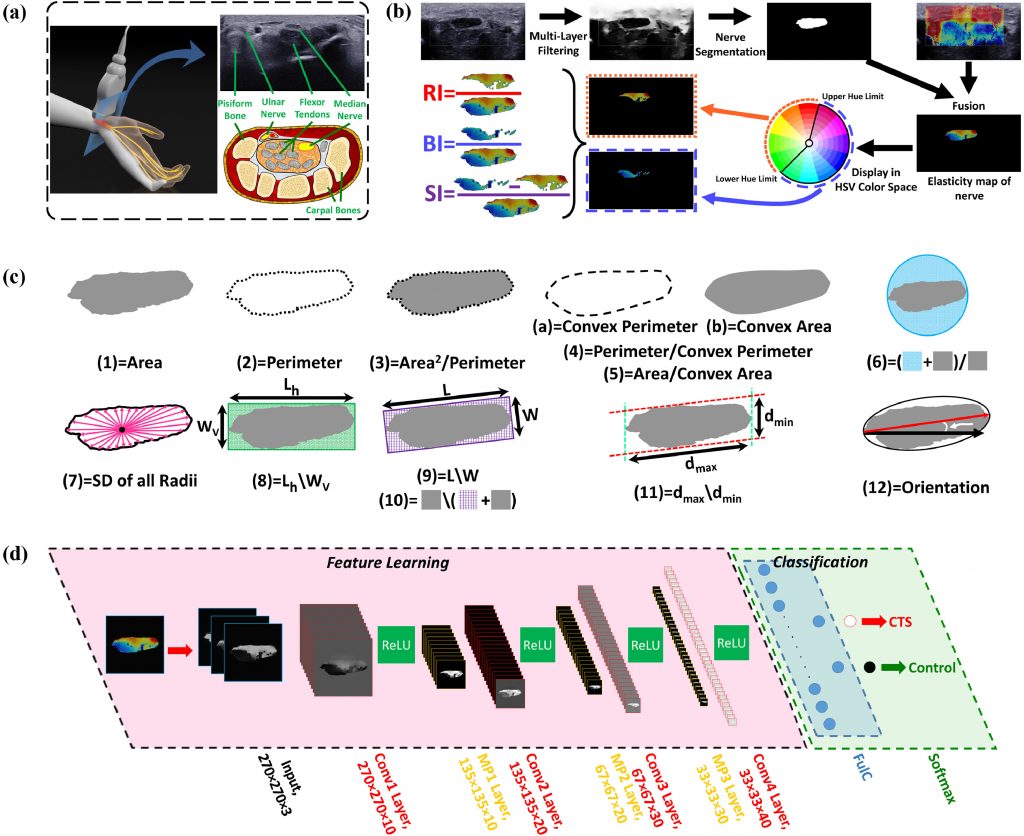
Abstract
Ultrasonography is an acceptable modality to evaluate median nerve (MN) in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Additional investigations are needed to evaluate sonographic parameters and compare their performances with artificial intelligence (AI) methods. The aim of this study is to compare the performance of shear wave elastography, morphometry, and AI techniques to predict MN entrapment accurately. 200 wrists including 100 CTS and 100 control wrists were included. Twelve morphological and five elasticity parameters were measured from each MN. Two AI techniques namely, support vector machine (SVM), and convolutional neural network (CNN) were used to diagnose CTS. MN area with area under receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.949 and mean elasticity with AUC of 0.942 showed the highest performance to differentiate CTS from control wrists among morphological and elasticity parameters, respectively. The CNN achieved the best performance with AUC of 0.980, while SVM obtained AUC of 0.943 in testing dataset to diagnose CTC. MN is larger, stiffer, more irregular and extended in CTS patients. Deep learning technique yielded the highest performance in diagnosing CTS automatically. AI methods have vast potential to be implemented in clinical practice as an auxiliary tool for the assessment of CTS with high accuracy.